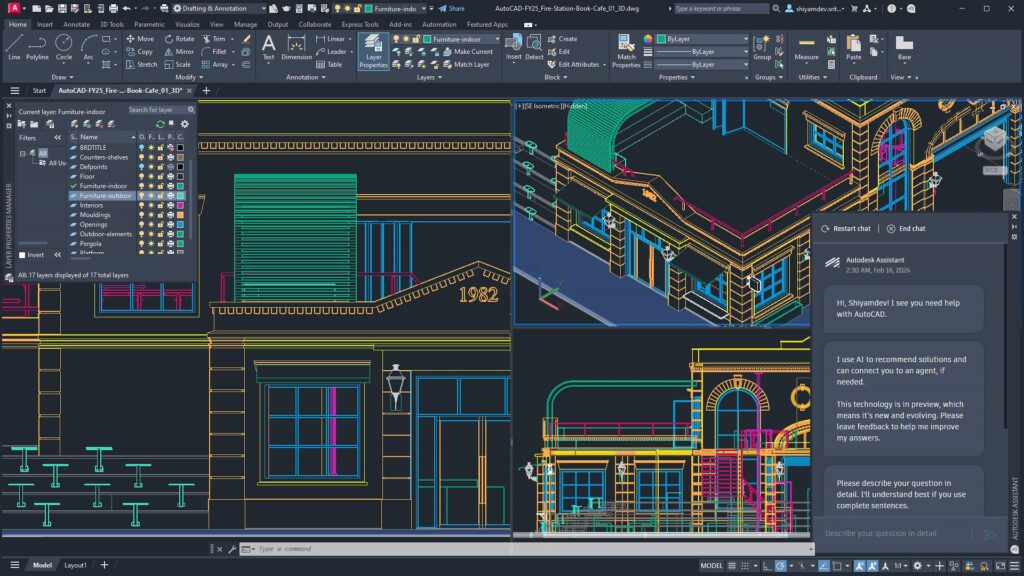
AutoCAD is a comprehensive CAD software application developed by Autodesk. It allows users to create 2D and 3D designs with high precision. Originally launched in 1982, AutoCAD has evolved significantly, incorporating advanced features and tools that cater to a broad range of professional needs.
1. Architectural Design
One of the primary uses of AutoCAD is in architectural design. Architects leverage AutoCAD to draft building plans, elevations, and sections with remarkable accuracy. The software’s ability to handle complex geometries and provide detailed documentation makes it invaluable for planning and constructing residential, commercial, and industrial structures.
2. Engineering Drafting
Engineers in various disciplines, including civil, mechanical, and electrical, rely on AutoCAD for drafting and designing. Civil engineers use AutoCAD to create detailed site plans and infrastructure layouts. Mechanical engineers employ it for designing machinery and components, while electrical engineers use it for creating wiring diagrams and circuit layouts. The software’s precision and flexibility streamline the engineering design process, ensuring that all components fit together seamlessly.
3. Product Design and Manufacturing
In product design and manufacturing, AutoCAD plays a crucial role. Designers use it to create detailed product models and prototypes. Its 3D modeling capabilities allow for visualizing and testing designs before physical production begins. This not only speeds up the design process but also reduces the risk of costly errors in manufacturing.
4. Interior Design
Interior designers use AutoCAD to plan and visualize interior spaces. The software’s ability to create detailed floor plans, furniture layouts, and 3D renderings helps designers convey their vision to clients and contractors. With AutoCAD, interior designers can experiment with different design elements and ensure that every detail aligns with their aesthetic and functional goals.
5. Urban Planning
AutoCAD is also instrumental in urban planning and landscape architecture. Planners use it to develop detailed maps, zoning layouts, and landscape designs. The software’s advanced tools allow for the integration of various data sets, enabling planners to create comprehensive and cohesive urban spaces.
6. Construction Documentation
AutoCAD excels in generating precise construction documentation. Detailed drawings, specifications, and annotations can be created to guide the construction process. This documentation ensures that all stakeholders are on the same page and helps to prevent misunderstandings and errors during construction.
7. Custom Design and Automation
AutoCAD offers customization options through scripting and automation. Users can create custom commands, automate repetitive tasks, and tailor the software to specific project needs. This level of customization enhances productivity and allows for more efficient workflows.
Benefits of Using AutoCAD
- Precision and Accuracy: AutoCAD’s precision tools ensure that every detail is accurate, reducing the risk of errors in the final design.
- Versatility: Whether you’re working on a building, a machine, or an interior space, AutoCAD’s versatile features cater to a wide range of design needs.
- Efficiency: The software’s automation and customization capabilities streamline design processes, saving time and effort.
- Collaboration: AutoCAD’s support for various file formats and its integration with other software facilitate collaboration among team members and stakeholders.
- Visualization: 3D modeling and rendering tools allow for realistic visualizations, helping designers and clients to better understand the final product.
